Operate a Hydra node
This page guides Hydra users on troubleshooting issues when running their instances of hydra-node and participating in a Hydra head.
Example setup
We offer sample node configurations that will help you get started with hosting a Hydra node on virtual machines in the cloud. These configurations are available in the sample-node-config/ directory.
Google Cloud with Terraform
This setup includes a docker-compose.yaml file, which serves as a robust template for configuring cardano-node and hydra-node services. Also, various scripts are provided to help you set up your cluster.
Logs
Following the principles outlined in ADR-9, the hydra-node emits JSON formatted logs to the stdout stream, with one log item per line.
Monitoring
When the --monitoring-port PORT argument is provided, the hydra-node executable will expose a Prometheus compatible HTTP /metrics endpoint on the specified port to enable metrics scraping.
For instance, if a hydra-node is initiated with --monitoring-port 6001, the following command:
curl http://localhost:6001/metrics
will output:
# TYPE hydra_head_confirmed_tx counter
hydra_head_confirmed_tx 0
# TYPE hydra_head_inputs counter
hydra_head_inputs 50467
# TYPE hydra_head_peers_connected gauge
hydra_head_peers_connected 0.0
# TYPE hydra_head_requested_tx counter
hydra_head_requested_tx 0
# TYPE hydra_head_tx_confirmation_time_ms histogram
hydra_head_tx_confirmation_time_ms_bucket{le="5.0"} 0.0
hydra_head_tx_confirmation_time_ms_bucket{le="10.0"} 0.0
hydra_head_tx_confirmation_time_ms_bucket{le="50.0"} 0.0
hydra_head_tx_confirmation_time_ms_bucket{le="100.0"} 0.0
hydra_head_tx_confirmation_time_ms_bucket{le="1000.0"} 0.0
hydra_head_tx_confirmation_time_ms_bucket{le="+Inf"} 0.0
hydra_head_tx_confirmation_time_ms_sum 0.0
hydra_head_tx_confirmation_time_ms_count 0
[!NOTE] Note that
hydra_head_peers_connectedwill count down if the number of online peers is greater thantotal_peers/2. After that, if another peer goes offline, it will drop to0, to indicate that etcd consensus is broken.
Common issues
No head is observed from the chain
- Ensure the
hydra-nodeis connected to acardano-nodeoperating on the correct network. Verify the--networkcommand-line argument and thecardano-nodeconfiguration. - Remember, the
hydra-nodecannot start if it cannot connect to thecardano-node, which might require time as thecardano-nodemust revalidate its database and potentially reconstruct its ledger state upon startup. Its connections are not open until it is fully prepared. If running as a service or a container, ensure that the orchestrator restarts the process when it crashes. - Check that the Scripts transaction identifier is valid. This identifier is provided on the release page for the three major networks (
preview,pre-production,mainnet). - Verify that the
hydra-node's Cardano signing key is consistent with the Verification key from theInittransaction. Ensure the--cardano-signing-keyparameter points to the correct key, and that peers have the accurate--cardano-verification-keyfor your node. - Confirm that peers' Cardano verification keys are accurate. This mirrors the above issue; check parameters on all peers.
Head does not make progress
- Confirm peers are properly connected to each other. Verify the
--peerarguments point to the correcthost:portfor each peer. ThePeerConnectedmessage should be observed by the client or appear in the logs and be consistent across all peers involved in a head. - Ensure the Hydra signing key for your node or the Hydra verification keys for peers match each node's expectations. Verify that
AckSnmessages are received by all parties and that theLogicOutcomelog contains no errors.
Head Stuck: Peer Out of Sync
Processing transactions in a Hydra head requires each node to agree on transactions, which occurs when they sign a snapshot during the AckSn phase. The protocol validates transactions (on the NewTx command) against its local view of the ledger state, using the provided --ledger-protocol-parameters. Since transaction validity depends on configuration (and, to some extent, the exact build versions of hydra-node), one node may accept a transaction while its peers reject it.
When this happens, the accepting node's local state diverges from the rest, potentially leading to attempts to spend outputs that other nodes do not recognize as available.
This issue can also arise if a peer goes offline while a transaction is submitted, potentially causing the Hydra head to become stuck and preventing further snapshots from being signed (see test case).
As a result of this divergence, the local ledger state of each Hydra node essentially becomes forked, resulting in inconsistent states across the network. While it is technically still possible to submit transactions to the Hydra nodes, doing so is ineffective because snapshots do not update unless all nodes sign them. Each node starts accepting transactions based on entirely different states, leading to disagreement on which UTxOs have been spent.
To recover from this issue, we introduced side-loading of snapshots to synchronize the local ledger state of the Hydra nodes. With this mechanism, every peer reverts to the latest confirmed snapshot. This can be done by using latest snapshot confirmed from GET /snapshot to call the POST /snapshot endpoint, which clears the peer’s local pending transactions and restores its state to match the last agreed snapshot, allowing the node to rejoin the consensus with the rest of the network.
Newer confirmed snapshots can also be adopted if all party members use the POST /snapshot endpoint with the same ConfirmedSnapshot as the JSON body.
It is important to note that this recovery process is a coordinated effort among peers to ensure the consistency and availability of the Hydra head.
Run the Node on High Availability Using Mirror Nodes
If you are concerned about one of the nodes disappearing entirely; i.e. complete computer failure with no backup, then you might be interested in running "mirror nodes". While it is recommend that you would maintain backups of the persistence folder (along with your keys!), you can choose to follow the mirror-node technique in any case as yet another measure to ensure operation in the disastrous loss of a peer. Note further that this technique increases availability, but has a cost in that it requires storing your key material in two places.
Ensuring high availability in a Hydra Head can be achieved by using mirror nodes, allowing the same party to participate from multiple machines.
This setup enhances redundancy and fault tolerance, ensuring protocol continuity even if a node fails, as another node can take over signing snapshots if one becomes unavailable.
A mirror node operates with the same party credentials (Cardano and Hydra keys) as the original node, enabling it to sign L2 snapshots and perform L1 operations like Init, Commit, Close, Contest, FanOut, and Increment/Decrement funds from the head.
Note, each node must be configured as follows:
- with a unique
--node-id.- with a unique
--advertiseIP address, as they run on separate machines.- specify each original and mirror node with its unique
--peerIP address being advertised.- must not duplicate
--cardano-verification-keyand--hydra-verification-key, as these identify unique parties independently of their peer setup.- mirror nodes must use the same
--hydra-signing-keyand--cardano-signing-keyas their original counterpart.
Mirror nodes coexist alongside their original counterpart without conflict, although some duplication of Hydra network messages sent and received from the mirror is expected.
Occasionally, operators might observe a SnapshotAlreadySigned log, which is raised when both the mirror and the original party attempt to sign the same snapshot. This log is transient, harmless, and can be safely ignored.
Beyond the Hydra Head protocol, mirror nodes impact the underlying etcd cluster, which follows the Raft consensus protocol.
The cluster remains healthy only if a majority of nodes (
⌊n/2⌋ + 1) are online.
If too many nodes (including mirrors) go offline, the etcd cluster may become unresponsive, even if the Hydra protocol itself remains operational.
For instance, in a cluster with 3 Alice nodes (2 mirrors) and 1 Bob node:
- The Hydra Head protocol remains functional as long as all unique party keys are active.
- However, if 2 Alice nodes go down, the etcd cluster becomes unhealthy due to an insufficient active quorum.
To maintain both Hydra network stability and a functional etcd quorum, the number of mirrors (k) should always be fewer than half of the total nodes (n): k < ⌊n/2⌋.
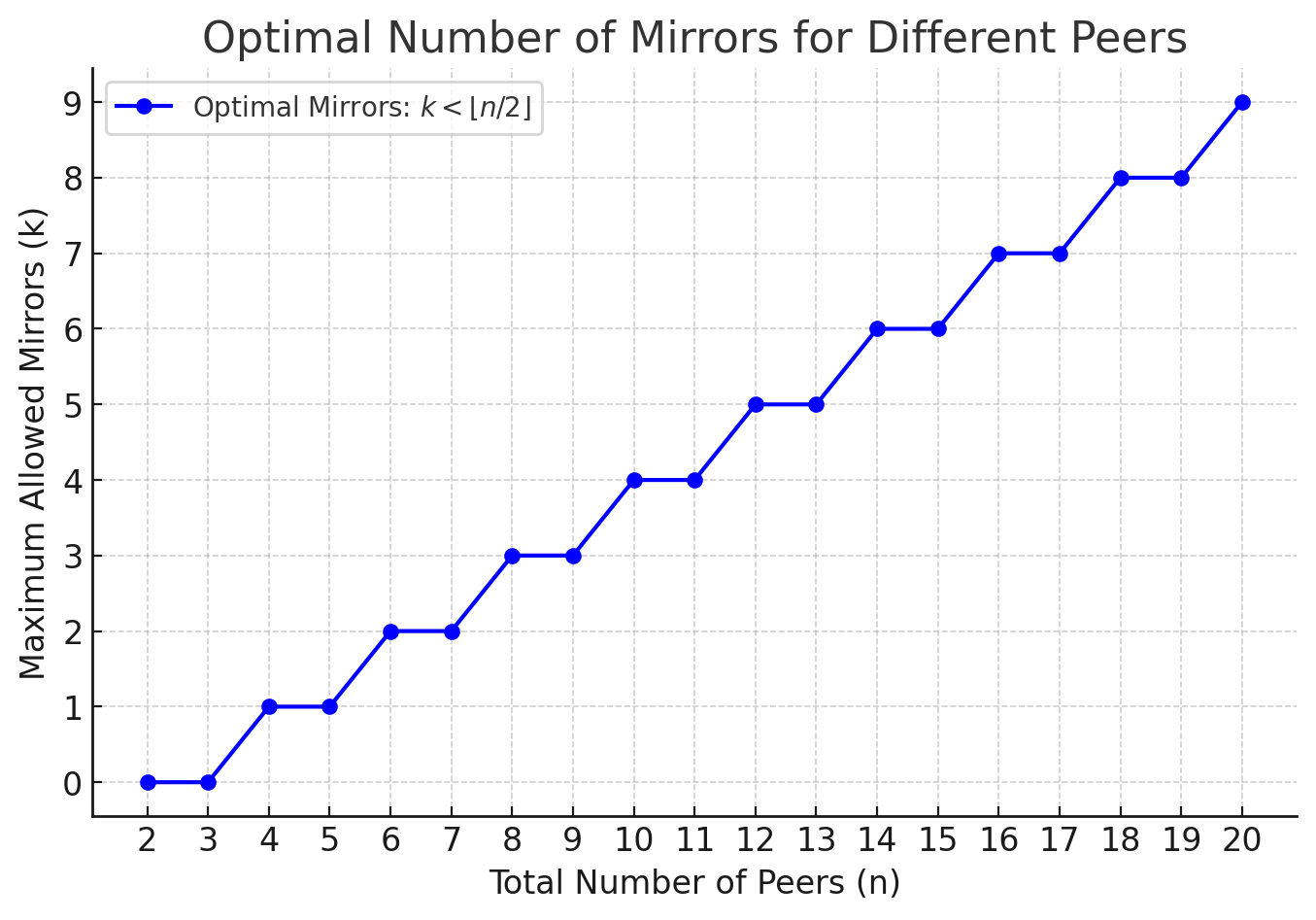
As you can see, the optimal number of mirrors in the cluster should be less than half of the total number of peers. This ensures the etcd cluster remains responsive and functional while still benefiting from high availability.

